After finding the SEPT product you want to
purchase, click on BUY and the system will transfer
you to the NORMADOC store which provides the fulfillment process for SEPT.
Every checklist is available in PDF or word format. The latter format allows you to adapt the checklist to your business case and/or a media of your choice such as a web-based excel worksheet. This enables you to demonstrate compliance with the standard in a manner that is most efficient for you.
Every checklist comes with four hours of free consultation. SEPT will answer any question concerning the standard or checklist for 60 days after purchase.
Checklist for - ISO 9001:2015, Quality Management Systems - Requirements.
Author: Andy Coster Pages: 178
Required Artifacts
| Procedures | Plans | Records | Documents | Audits | Reviews | Total |
| 1 | 5 | 38 | 13 | 2 | 18 | 77 |
The process of defining what is necessary for compliance with a quality management process standard such as "ISO Standard 9001:2015" is often confusing and laborious because the directions contained in the standards are unclear or ambiguous. To aid in determining what is actually "required" by the document in the way of physical evidence of compliance, the experts at SEPT have produced this checklist. This checklist is constructed around a classification scheme of physical evidence comprised of policies, procedures, plans, records, documents, audits, and reviews. There must be an accompanying record of some type when an audit or review has been accomplished. This record would define the findings of the review or audit and any corrective action to be taken. For the sake of brevity this checklist does not call out a separate record for each review or audit. All procedures should be reviewed but the checklist does not call out a review for each procedure, unless the standard calls out the procedure review. In this checklist "manuals, reports, scripts and specifications" are included in the document category. When the subject standard references another standard for physical evidence, the checklist does not call out the requirements of the referenced standard.
The Author has carefully reviewed the document "ISO Standard 9001:2015 Quality management systems - Requirements" and defined the physical evidence required based upon this classification scheme. SEPT has conducted a second review of the complete list to ensure that the documents' producers did not leave out a physical piece of evidence that a "reasonable person" would expect to find. It could certainly be argued that if the document did not call it out then it is not required; however if the standard was used by an organization to improve its process, then it would make sense to recognize missing documents. Therefore, there are documents specified in this checklist that are implied by the standard, though not specifically called out in the document, and they are designated by an asterisk (*) throughout this checklist. If a document is called out more than one time, only the first reference is stipulated.
There are occasional situations in which a procedure or document is not necessarily separate and could be contained within another document. For example, the "Design and Development Verification Plan" could be a part of the "Design and Development Plan". The Author has called out these individual items separately to ensure that the organization does not overlook any facet of physical evidence. If the organization does not require a separate document, and an item can be a subset of another document or record, then this fact should be denoted in the detail section of the checklist for that item. This should be done in the form of a statement reflecting that the information for this document may be found in section XX of Document XYZ. If the organizational requirements do not call for this physical evidence for a particular project, this should also be denoted with a statement reflecting that this physical evidence is not required and why. The reasons for the evidence not being required should be clearly presented in this statement. Further details on this step are provided in the Detail Steps section of the introduction. The size of these documents could vary from paragraphs to volumes depending upon the size and complexity of the project or business requirements.
General Principles of SEPT Checklist for the ISO Standard 9001:2015 Quality management systems - Requirements
This checklist was prepared by analyzing each clause of this document for the key words that signify a:
- Policy
- Procedure
- Plan
- Records
- Document (Including Manuals, Reports, and Specifications)
- Audit
- Review
This checklist specifies evidence that is unique. After reviewing the completed document, the second review was conducted from a common sense "reasonable man" approach. If a document or other piece of evidence appeared to be a required artifact, but was not called out in the document, then it is added with an asterisk (* - suggested artifacts) after its notation in the checklist. The information was transferred into checklist tables, based on the type of product or evidence.
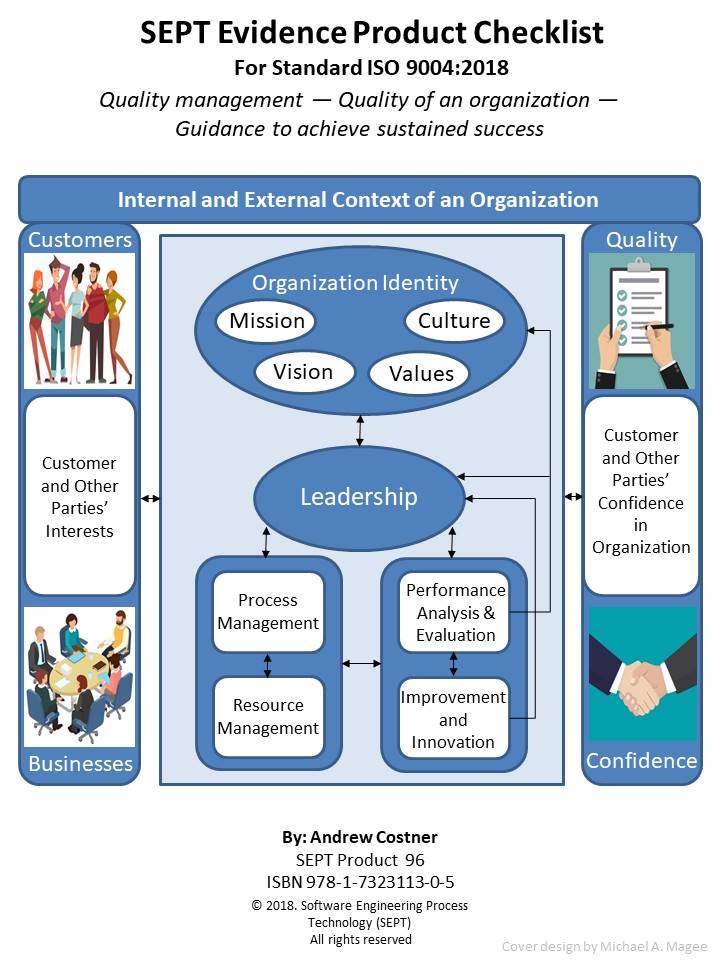
Checklist for - ISO 9004:2018 -- Quality of an Organization -- Guidance to Achieve Sustained Success
Author: Andy Coster Pages: 241
For 20 + years Software Engineering Process Technology (SEPT) has produced checklists for standards that address software issues. To reduce the fog surrounding these types of standards SEPT has produced checklists for standards since 1994. This is another checklist related to quality standards.
ISO 9004 will provide your organization with guidance and support to achieve sustained success by using a quality management approach. This approach can be used by any organization, regardless of size, type and activity. To document that an organization has achieved a certain quality maturity level the standard recommends that the organization produce and use certain quality artifacts (Procedure, Policy, Plan, Records, Document, Audits and Review) at each maturity level. However, what constitutes physical evidence (Artifacts) to meet the guidance outlined in ISO 9004 is sometimes difficult to identify. To bridge this gap the author and SEPT experts have identified items of physical evidence called out in the standard based on their knowledge of the document and their experience in the quality field. Each item of physical evidence that was identified by these experts is listed in the checklist as; policy, procedure, plan, records, document or reviews.
ISO 9004 promotes self-assessment as an important tool for the review of the maturity level of an organization. This self-assessment can provide an overall view of the performance of an organization and degree of maturity of their management system. To aid in this transition from physical evidence to maturity level, the checklist identifies the maturity level associated with each piece of physical evidence called out in the checklist. Since the standard does not assign a maturity level to an item of physical evidence the author and SEPT experts have assigned a maturity level to each piece of physical evidence listed. The maturity level is marked in brackets () after the artifact in each checklist. This assigning of maturity level was based on the expert knowledge of the standard and their experience in the quality field.
The SEPT checklists are constructed around a classification scheme of physical evidence comprised of policies, procedures, plans, records, documents, audits, and reviews. There must be an accompanying record of some type when an audit or review has been accomplished. This record would define the findings of the review or audit and any corrective action to be taken. For the sake of brevity this checklist does not call out a separate record for each review or audit. All procedures should be reviewed but the checklist does not call out a review for each procedure, unless the standard calls out the procedure review. In this checklist, "manuals, reports, scripts and specifications" are included in the document category. In the procedure category, guidelines are included when the subject standard references another standard for physical evidence. The checklist does not call out the requirements of the referenced standard.
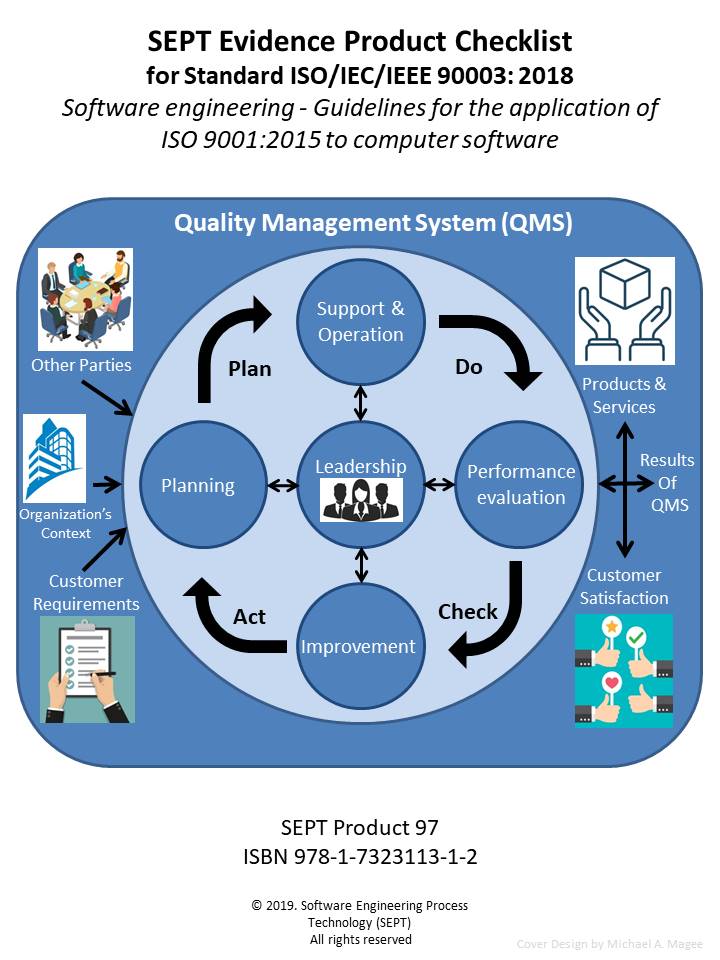
Checklist for - ISO/IEC/IEEE 90003:2018, Software Engineering. Guidelines for the application of ISO 9001:2015 to computer software.
Author: Andy Coster Pages: 279
ISO/IEC/IEEE 90003 will provide your organization with guidance and support to meet the requirements of ISO 9001:2015 for systems and software developed, operated or maintained by your organization. This standard can be used by any organization, regardless of size, type and activity. To document that an organization has met the requirements of ISO 9001:2015, the standard recommends that the organization produce and use certain quality artifacts (Procedure, Policy, Plan, Records, Document, Audits and Review). However, what constitutes physical evidence (Artifacts) to meet the guidance outlined in ISO/IEC/IEEE 90003 is sometimes difficult to identify. To bridge this gap the author and SEPT experts have identified items of physical evidence called out in the standard based on their knowledge of the document and their experience in the quality field. Each item of physical evidence that was identified by these experts is listed in the checklist as; policy, procedure, plan, records, document, audits or reviews.
The SEPT checklists are constructed around a classification scheme of physical evidence comprised of policies, procedures, plans, records, documents, audits, and reviews. There must be an accompanying record of some type when an audit or review has been accomplished. This record would define the findings of the review or audit and any corrective action to be taken. For the sake of brevity this checklist does not call out a separate record for each review or audit. All procedures should be reviewed but the checklist does not call out a review for each procedure, unless the standard calls out the procedure review. In this checklist, "manuals, reports, scripts and specifications" are included in the document category. In the procedure category, guidelines are included when the subject standard references another standard for physical evidence. The checklist does not call out the requirements of the referenced standard.
The author has carefully reviewed the Standard ISO/IEC/IEEE 90003:2018 and defined the physical evidence required based upon this classification scheme. Sept's engineering department has conducted a second review of the complete list and baseline standard to ensure that the documents' producers did not leave out a physical piece of evidence that a "reasonable person" would expect to find. If an artifact is called out more than one time, only the first reference is stipulated. If an artifact is required by ISO 9001:2015 it appears in the checklist without appended symbol. If an item is "suggested" by ISO 9001:2015 it appears with an appended asterisk (*). If an item is "suggested" by ISO/IEC/IEEE 90003 guidelines it appears in the checklist with an appended hash (#). In this way traceability of requirements and suggested items to both standards is possible.
Note: These notations are listed in the footnotes for each section
The SEPT checklists are constructed around a classification scheme of physical evidence comprised of policies, procedures, plans, records, documents, audits, and reviews. There must be an accompanying record of some type when an audit or review has been accomplished. This record would define the findings of the review or audit and any corrective action to be taken. For the sake of brevity this checklist does not call out a separate record for each review or audit. All procedures should be reviewed but the checklist does not call out a review for each procedure, unless the standard calls out the procedure review. In this checklist, "manuals, reports, scripts and specifications" are included in the document category. In the procedure category, guidelines are included when the subject standard references another standard for physical evidence. The checklist does not call out the requirements of the referenced standard.
A Checklist for Assessing Software Suppliers Compliance With ISO/IEC 90003:2014.
Authors: Andy Coster Pages: 35
The purpose of this checklist is to assist a company to determine if their software suppliers meet the requirements of the ISO/IEC 90003:2014 standard, " "Software engineering: Guidelines for the application of ISO 9001:2008 to computer software."
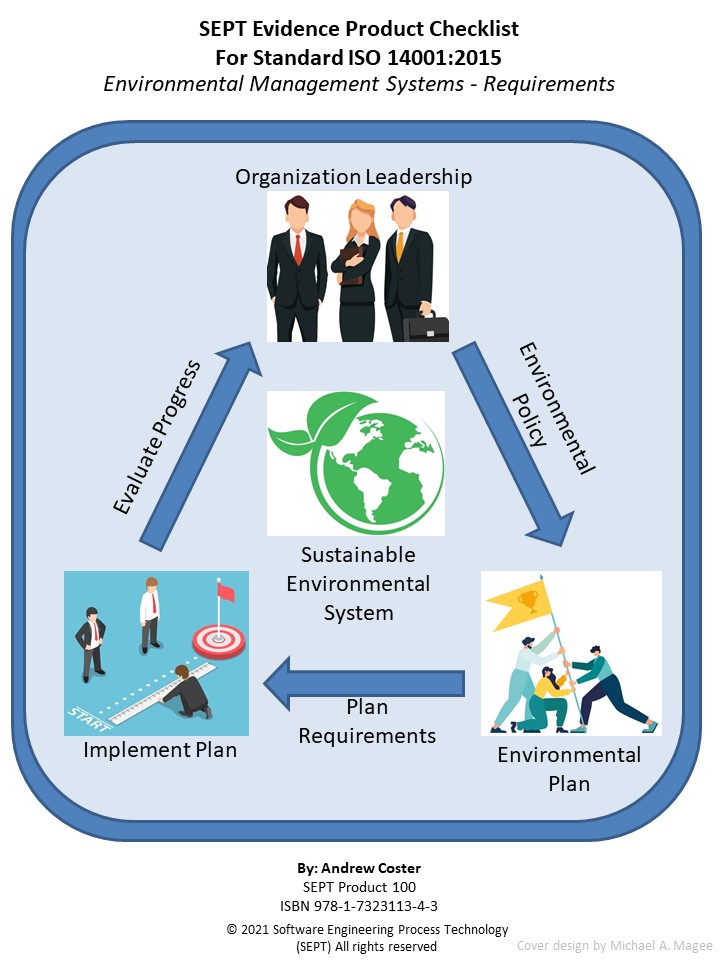
Checklist for ISO 14001:2015 Environmental Management Systems — Requirements with Guidance for Use
Author: Andy Coster Pages: 105
For 25+ years Software Engineering Process Technology (SEPT) has produced checklists for international standards. They have been produced for Medical Devices, Quality, Security and Software processes.
Organizations buy and use these checklists for:
- Performing a gap analysis - “Standard requirement” versus “what the organization does”,
- Ensuring that all the artifacts that are cited in the standard are addressed,
- Providing the traceability by artifact from the standard to a process step,
- Demonstrating that the organization was following an international standard in case of litigation,
- Reducing cost by purchasing a checklist instead of developing one internally, and
- Providing insurance that they have a checklist that is compiled by a company experienced in deciphering international standards and verified by domain experts.
This is a checklist for standard ISO 1400:2015. The purpose of the
checklist is to define clearly all the artifacts (policies,
procedures, plans, records, documents, audits, or reviews) that
the underlying standard calls out. Furthermore, what constitutes
physical evidence (Artifacts) to meet the guidance outlined in
ISO 14001 is sometimes difficult to identify. To bridge this
gap the author and SEPT experts have identified items of
physical evidence called out in the standard based on their
knowledge of the document and their experience in the standards
field. Each item of physical evidence that was identified by
these experts is listed in the checklist as an artifact
(policies, procedures, plans, records, documents, audits, or
reviews).
The author has carefully reviewed the document “ISO
Standard 14001:2015 Environmental Management – Requirements"
and defined the physical evidence required based upon this
classification scheme. SEPT has conducted a second review
of the complete list to ensure that the documents’
producers did not leave out a physical piece of evidence
that a “reasonable person” would expect to find.
It could certainly be argued that if the document did not call
it out then it is not required; however, if the standard was
used by an organization to improve its process, then it would
make sense to recognize missing documents. Therefore, there
are documents specified in this checklist that are implied
by the standard, though not specifically called out in the
standard.
This checklist was prepared by analyzing each clause of this document for the key words that signify a:
- Policy
- Procedure
- Plan
- Records
- Document (Including Manuals, Reports, and Specifications)
- Audit
- Review
This checklist specifies evidence that is unique. After reviewing
the completed document, the second review was conducted from a common
sense “reasonable person” approach. If a document or
other piece of evidence appeared to be required, but was not called
out in the document, then it is added with an asterisk (*) after its
notation in the checklist. The information was transferred into
checklist tables, based on the type of product or evidence.
Required items are denoted by an underline to aid use of the
checklist.
When a company is planning to use "ISO 14001:2015 Environmental
Management Systems – Requirements" standard, the company
should review the evidence checklist. If the company’s
present process does not address an ISO 14001:2015 standard
item, then this question should be asked: Is the evidence
item required for the type of business of the company?
If in the view of the company the evidence is not required,
the rationale should be documented and inserted in the checklist
and Environmental manual. This rationale should
pass “the reasonable person rule.” If
the evidence is required, plans should be prepared to address
the missing item(s).
There are artifacts specified in this checklist that are implied by the standard, though not specifically called out in the standard, and they are designated by an asterisk (*) throughout this checklist.
In total, there are 246 artifacts included in the SEPT ISO 14001 checklist.
|